Henry Becquerel and the spouses Pierre and Marie Curie.

At the end of the 19th century, researchers Henry Becquerel, and Mr and Mrs Pierre and Marie Curie, with experimental physics they discovered unprecedented physical phenomena which they then baptized with the name of radioactivity. They ascertained that some minerals, containing uranium and radium had the property of impressing photographic plates which thus showed various dark spots.
For this particular property, Uranium, Radium and Polonius (the last two were discovered by Pierre and Marie Curie), they were called "active" while the phenomenon of spontaneous emission of particles was called radioactivity.
Since then, almost 2500 different nuclei species have been identified and only a small percentage, circa 280, they were stable.
Becquerel had discovered that the element uranium emitted invisible radiation (1896). The Curie couple then began to study the radiation emitted by uranium and managed to isolate two new elements which, like uranium,, they emitted radiation.
They were called Polonius (in honor of Poland, Marie's homeland) and Radio. Marie Curie called the chemical elements radioactive, like radium, they emit radiation.
From then on, a new branch of physics was born which was called Radioactivity which deals with the properties of radioactive elements. Thanks to their discoveries, the Curie couple obtained the Nobel Prize in physics in 1903.
Pierre Curie died on 19 April 1906 after falling from a moving carriage. His wife instead died of cancer, caused by excessive exposure to radiation, on June 4, 1934.
The three types of nuclear radiation
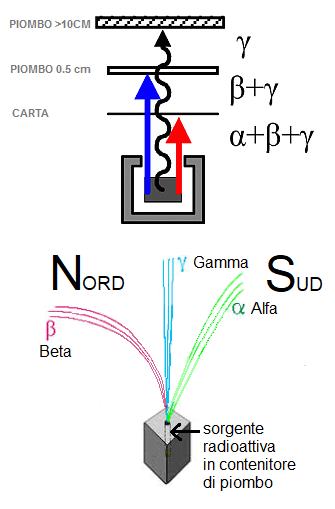
In nature there are three types of more or less ionizing radiation which are distinguished by their atomic origin and unequivocal behavior.
We have α radiation (alfa) the most ionizing of the three categories having a positive charge +2 which can be easily deflected by magnetic fields.
In practice these are helium atoms, which due to their non-negligible mass are very energetic and not very penetrating, in fact they can be stopped simply with a thin sheet of paper.
β Radiations (beta) with negative charge −1, that is, they are electrons, they are quite insightful, they can also be deflected by intense magnetic fields in the opposite direction of the Alphas and to stop them completely a layer of lead of about 0.5 cm is needed.
γ radiation (gamma), of a wave nature that behave like light, they are uncharged, they are not affected by magnetic fields and are very strong, penetrating and extremely dangerous, so much so that a layer of lead of at least 10 cm is required to block them.
The best Geiger counters made in Italy, True Italian excellence.
Guardian Ray Smart 2.8p Professional Geiger Counter with WiFi, Bluetooth, microSD, Touch Color LCD and Pancake probe.
€1.259,00Add to cart
Contatore Geiger MINIGEIGER 7317 con sonda Pancake
€959,00 – €1.590,00Select options- Sale!

Micro Geiger – Contatore Geiger per Smartphone Android
€350,00Original price was: €350,00.€330,00Current price is: €330,00.Add to cart 
GMC 300E PLUS Economic Geiger Counter
€159,00Read more
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
