Radon is a very radioactive gas, belonging to the family of so-called noble or inert gases. E' tanto pericoloso quanto insidioso poiché non può essere percepito con i normali sensi in quanto risulta incolore, odorless and tasteless.

Radon produces itself “nuclear decay” of the Radius, another very radioactive element which in turn derives from the decay of Uranium.
These elements have always been present in nature in different quantities in the earth's crust. Therefore it can also be present in building materials as the components with which they are made are extracted from the same earth.
We can find it in percentages almost always contained in cement, in the tuff, in bricks, in pozzolana, in granites, etc.). Radon-222 has a half-life of 3,82 days and drifting, by alpha decay, from the decay of Uranium-238 into Radium-226
Radon is dangerous for your health?
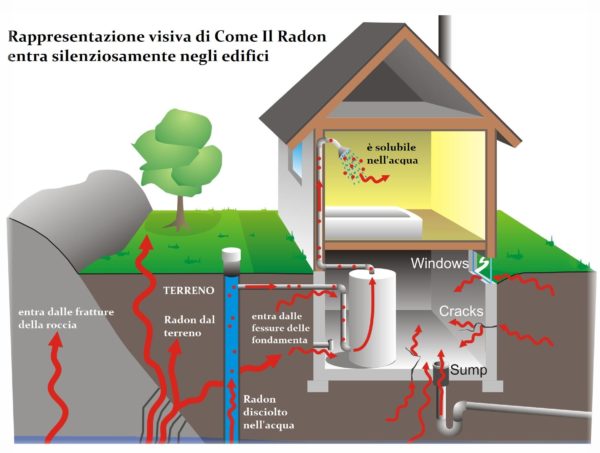
The World Health Organization has identified Radon as the second risk factor for the onset of lung cancer.
In Italy it is estimated that Radon causes up to 6.000 victims every year, while in the USA one home in every 15 is considered to be at risk of Radon.
E’ a noble gas, which is much heavier than air and is also soluble in water, for these reasons from the soil or building materials where it originates, it propagates easily and can spread into buildings, exploiting small cracks and porosity in the floors.
So he manages to silently invade the premises, accumulating especially in the sub-floors and basements.
In Italy there is not yet a law that sets the maximum permitted limit of radon concentration in private homes.
However, reference is made to the levels recommended by the European Community, which are of: 200 Bq/m³ for new homes and: 400 Bq/m³ for those already existing.
For work environments, however, Italy with the Legislative Decree of 26 May 2000, n. 241 sets a maximum level of 500 Bq/m³. Relative contribution of various radioactive sources.
The National Institute of Nuclear Physics explains it as the most significant contribution to environmental radioactivity in the places where we live, it is over 60%, determined by Radon gas.
Then secondly there are other smaller sources of radiation, which instead depend on the materials that surround us (tuff, granites, etc.), which are generally often present in our own home. In practice there is no place in the world where radon is not present.
Outdoors it cannot reach high concentrations, but in closed places (especially in the basements), it can reach high concentrations that put people's health at risk. The products originating from its nuclear decay are also very radioactive, and if inhaled they can cause serious damage to the respiratory tract.
Where can radon be found?.
Radon is widespread everywhere in the earth's crust and can be found dissolved in water and in numerous rocks of volcanic origin., like granites, pozzolana, spit, make.
However, the concentration varies depending on the area, therefore in some areas particularly high radon levels can be recorded.
Outdoors it tends to disperse rapidly but in water things are very different because it can be present in the form of a dissolved gas, thus becoming more dangerous.
In fact, it can be transported by waterways even over long distances, with the probability that it could then flow into the aquifers.
What kind of buildings are most at risk from Radon
The presence of radon could be found in homes built on granitic or volcanic soil, that is, near volcanoes or on soil rich in tuff.
It can also be found in buildings whose foundations have been laid directly on the ground, basement rooms and cellars. In constructions made with granite-based clays, tuff, porphyry, lava stones and cements of pozzolanic origin.
Therefore it is clear that in Italy the materials most at risk are pozzolana, peperino from Lazio and tuff from Campania.
Obviously the concentration of Radon is greater on the lower floors, but it also manages to spread to the upper floors.
The natural temperature differences between the lower and higher floors create convective motions that allow the gas to rise.
This occurs especially in winter when the heating is turned on, through the presence of the ascending currents that are created in the flues, and in the extraction systems of bathrooms and kitchens.
In this case, adequate and constant ventilation of the rooms is recommended.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
